Research on minimally invasive hip replacement surgery is mixed, and it is not clear whether it has an advantage over traditional hip replacement surgery. 1 Jayankura M, Potaznik A. Total hip arthroplasty by mini-approach: review of literature and experience of direct anterior approach on orthopaedic table. (Abstract only.) Rev Med Brux. 2011;32(6 Suppl):S76-83. Review. French. PubMed PMID: 22458062. , 2 Repantis T, Bouras T, Korovessis P. Comparison of minimally invasive approach versus conventional anterolateral approach for total hip arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. (Abstract only.) Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015 Jan;25(1):111-6. doi: 10.1007/s00590-014-1428-x. Epub 2014 Feb 21. PubMed PMID: 24557411. , 3 Yang B, Li H, He X, Wang G, Xu S. Minimally invasive surgical approaches and traditional total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of radiological and complications outcomes. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37947. Epub 2012 May 24. PubMed PMID: 22655086; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3360020. , 4 American Academy of Orthopeadic Surgeons. "Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement." OrthoInfo. Last reviewed August 2007. http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=A00404 Last Reviewed June 2014. Accessed January 20, 2015. , 5 Imamura M, Munro NA, Zhu S, Glazener C, Fraser C, Hutchison J, Vale L. Single mini-incision total hip replacement for the management of arthritic disease of the hip: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012 Oct 17;94(20):1897-905. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.K.00495. PubMed PMID: 23079882. , 6 Migliorini F, Biagini M, Rath B, Meisen N, Tingart M, Eschweiler J. Total hip arthroplasty: minimally invasive surgery or not? Meta-analysis of clinical trials. Int Orthop. 2019 Jul;43(7):1573-1582. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-4124-3. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Review. PubMed PMID: 30171273. This area of ongoing research is an example of how the medical field is continually evolving and trying to improve outcomes for patients.
In the meantime, people considering hip replacement surgery and their surgeons must make decisions based on the information available.
In This Article:
- Minimally Invasive Total Hip Replacement
- Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement vs. Traditional Hip Replacement
- Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement Procedure
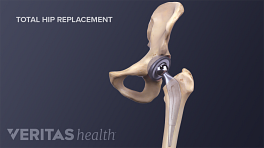
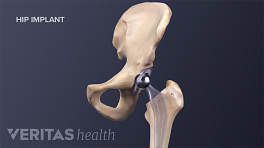
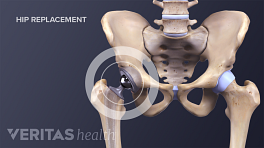
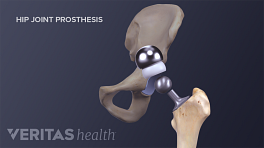
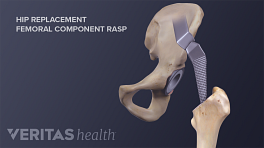
Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement Surgery
There is no single way to perform a minimally invasive hip replacement. Because of the limited research available, all minimally invasive techniques are grouped in this section. Typically, minimally invasive hip replacement surgery requires a single 3- to 6-inch incision or two smaller incisions.
Potential advantages
The minimally invasive approaches to hip replacement may provide:
- Smaller scar
- Less damage to surrounding soft tissue
- A faster rehabilitation, 7 Gollwitzer H. [The minimally invasive AMIS technique for total hip replacement : Video article]. Orthopade. 2018 Sep;47(9):782-787. doi: 10.1007/s00132-018-3591-y. Review. PubMed PMID: 29974162. , 8 Kutzner KP, Donner S, Schneider M, Pfeil J, Rehbein P. One-stage bilateral implantation of a calcar-guided short-stem in total hip arthroplasty : Minimally invasive modified anterolateral approach in supine position. Simultan-bilaterale Implantation einer kalkargeführten Kurzschaftprothese : Minimal-invasiver anterolateraler Zugang in Rückenlage. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2017;29(2):180–192. doi:10.1007/s00064-016-0481-5 though research in this area is mixed 5 Imamura M, Munro NA, Zhu S, Glazener C, Fraser C, Hutchison J, Vale L. Single mini-incision total hip replacement for the management of arthritic disease of the hip: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012 Oct 17;94(20):1897-905. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.K.00495. PubMed PMID: 23079882. , 9 Li N, Deng Y, Chen L. Comparison of complications in single-incision minimally invasive THA and conventional THA. Orthopedics. 2012 Aug 1;35(8):e1152-8. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20120725-12. PubMed PMID: 22868598. , 10 Foucher KC, Wimmer MA, Moisio KC, Hildebrand M, Berli MC, Walker MR, Berger RA, Galante JO. Time course and extent of functional recovery during the first postoperative year after minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty with two different surgical approaches--a randomized controlled trial. J Biomech. 2011 Feb 3;44(3):372-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2010.10.026. Epub 2010 Nov 13. PubMed PMID: 21075378.
- Less blood loss 6 Migliorini F, Biagini M, Rath B, Meisen N, Tingart M, Eschweiler J. Total hip arthroplasty: minimally invasive surgery or not? Meta-analysis of clinical trials. Int Orthop. 2019 Jul;43(7):1573-1582. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-4124-3. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Review. PubMed PMID: 30171273.
It is not clear if the reduced blood loss is enough to offer meaningfully better results for patients. 5 Imamura M, Munro NA, Zhu S, Glazener C, Fraser C, Hutchison J, Vale L. Single mini-incision total hip replacement for the management of arthritic disease of the hip: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012 Oct 17;94(20):1897-905. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.K.00495. PubMed PMID: 23079882.
Potential disadvantages
Concerns about the minimally invasive approaches to hip replacement include:
- The surgeon has a limited view of the joint, making it more challenging for a surgeon to create a perfect fit and alignment for the hip replacement components
- Skin and soft tissue can be stretched and torn during surgery
- Possible increased likelihood of nerve damage 6 Migliorini F, Biagini M, Rath B, Meisen N, Tingart M, Eschweiler J. Total hip arthroplasty: minimally invasive surgery or not? Meta-analysis of clinical trials. Int Orthop. 2019 Jul;43(7):1573-1582. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-4124-3. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Review. PubMed PMID: 30171273.
Despite these potential disadvantages, most minimally invasive total hip replacements have successful outcomes.
Who can have minimally invasive hip replacement surgery
Patients must be healthy enough to undergo major surgery and be able to follow-through with pre- and post-surgical instructions. In addition, evidence seems to indicate that the best candidates—- Are younger
- Are relatively thin, not obese or very muscular
- Lack any bone or joint deformities
- Have not had previous hip surgery
- Do not have osteoporosis; osteoporosis increases the chance of bone breakage
Many patients will not meet these requirements.
Traditional Hip Replacement Surgery
Most hip replacements are traditional hip replacements. During this surgery, a surgeon makes a 6- to 10-inch incision and has a clear view of the hip joint to be operated on.
Potential advantages
Traditional approaches to hip replacement tend to:
- Use reliable and time-tested surgical techniques
- Provide the surgeon with a clear view of the hip joint, which may help them create an ideal fit and alignment
When the new hip’s components are well aligned, the chances for good pain relief and function improve and the likelihood of certain post-surgical complications occurring is reduced.
Potential disadvantages
When compared with minimally invasive surgery, traditional hip replacement is associated with:
- More damage to surrounding muscles and other soft tissues
- A slower recovery
- A larger scar
More tissue is cut during traditional surgery, so more healing needs to take place.
See Total Hip Replacement Surgery Risks and Complications
Who can have traditional hip replacement
As with minimally invasive surgery, traditional hip replacement patients must be healthy enough to undergo major surgery and be able to follow through with pre- and post-surgical instructions. In addition, candidates typically:- Are subject to less stringent weight requirements
- Can have mild to moderate osteoporosis
People with severe osteoporosis are typically not eligible for any joint replacement surgery.
See Indications and Eligibility for Total Hip Replacement Surgery
Hospital Stays Are About the Same
Hospital stays for traditional hip replacement have decreased in recent years, averaging about 1 to 2 days, with many patients being discharged in less than 24 hours. 11 Kelly MP, Calkins TE, Culvern C, Kogan M, Della Valle CJ, Inpatient versus Outpatient Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: Which has higher patient satisfaction?, The Journal of Arthroplasty (2018), doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2018.07.025. Research 6 Migliorini F, Biagini M, Rath B, Meisen N, Tingart M, Eschweiler J. Total hip arthroplasty: minimally invasive surgery or not? Meta-analysis of clinical trials. Int Orthop. 2019 Jul;43(7):1573-1582. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-4124-3. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Review. PubMed PMID: 30171273. suggests the average hospital stays for minimally invasive hip replacement surgeries are about the same.
See Total Hip Replacement Surgery Recovery
Cost Savings Vary
Some people believe minimally invasive hip replacement surgery cuts down on recovery time and therefore saves money. While this may be true, patients who are covered by Medicare or private insurance might see little to no out-of-pocket savings.
Patients may opt for minimally invasive surgery hoping they can return to work sooner, minimizing their financial burden. However, returning to work sooner is not guaranteed. A person’s return to work is dependent on the individual’s unique recovery as well as the type of work they do.
- 1 Jayankura M, Potaznik A. Total hip arthroplasty by mini-approach: review of literature and experience of direct anterior approach on orthopaedic table. (Abstract only.) Rev Med Brux. 2011;32(6 Suppl):S76-83. Review. French. PubMed PMID: 22458062.
- 2 Repantis T, Bouras T, Korovessis P. Comparison of minimally invasive approach versus conventional anterolateral approach for total hip arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. (Abstract only.) Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015 Jan;25(1):111-6. doi: 10.1007/s00590-014-1428-x. Epub 2014 Feb 21. PubMed PMID: 24557411.
- 3 Yang B, Li H, He X, Wang G, Xu S. Minimally invasive surgical approaches and traditional total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of radiological and complications outcomes. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37947. Epub 2012 May 24. PubMed PMID: 22655086; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3360020.
- 4 American Academy of Orthopeadic Surgeons. "Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement." OrthoInfo. Last reviewed August 2007. http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=A00404 Last Reviewed June 2014. Accessed January 20, 2015.
- 5 Imamura M, Munro NA, Zhu S, Glazener C, Fraser C, Hutchison J, Vale L. Single mini-incision total hip replacement for the management of arthritic disease of the hip: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012 Oct 17;94(20):1897-905. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.K.00495. PubMed PMID: 23079882.
- 6 Migliorini F, Biagini M, Rath B, Meisen N, Tingart M, Eschweiler J. Total hip arthroplasty: minimally invasive surgery or not? Meta-analysis of clinical trials. Int Orthop. 2019 Jul;43(7):1573-1582. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-4124-3. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Review. PubMed PMID: 30171273.
- 7 Gollwitzer H. [The minimally invasive AMIS technique for total hip replacement : Video article]. Orthopade. 2018 Sep;47(9):782-787. doi: 10.1007/s00132-018-3591-y. Review. PubMed PMID: 29974162.
- 8 Kutzner KP, Donner S, Schneider M, Pfeil J, Rehbein P. One-stage bilateral implantation of a calcar-guided short-stem in total hip arthroplasty : Minimally invasive modified anterolateral approach in supine position. Simultan-bilaterale Implantation einer kalkargeführten Kurzschaftprothese : Minimal-invasiver anterolateraler Zugang in Rückenlage. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2017;29(2):180–192. doi:10.1007/s00064-016-0481-5
- 9 Li N, Deng Y, Chen L. Comparison of complications in single-incision minimally invasive THA and conventional THA. Orthopedics. 2012 Aug 1;35(8):e1152-8. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20120725-12. PubMed PMID: 22868598.
- 10 Foucher KC, Wimmer MA, Moisio KC, Hildebrand M, Berli MC, Walker MR, Berger RA, Galante JO. Time course and extent of functional recovery during the first postoperative year after minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty with two different surgical approaches--a randomized controlled trial. J Biomech. 2011 Feb 3;44(3):372-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2010.10.026. Epub 2010 Nov 13. PubMed PMID: 21075378.
- 11 Kelly MP, Calkins TE, Culvern C, Kogan M, Della Valle CJ, Inpatient versus Outpatient Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: Which has higher patient satisfaction?, The Journal of Arthroplasty (2018), doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2018.07.025.