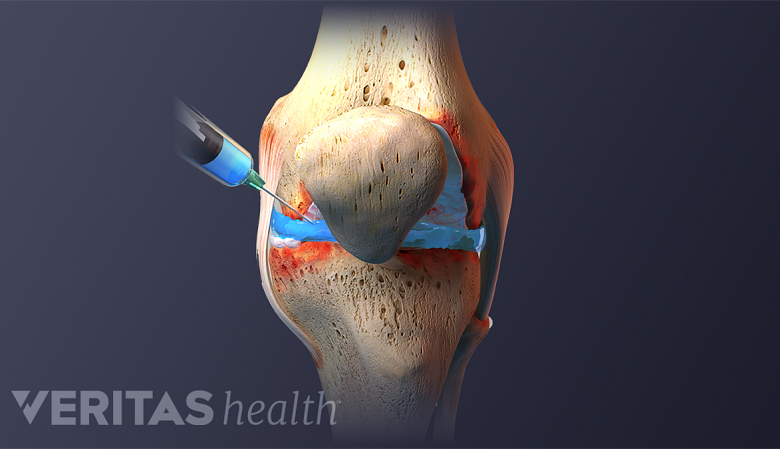
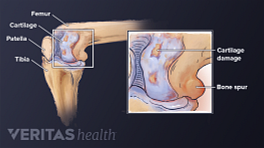
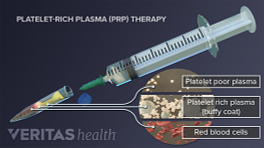
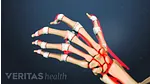
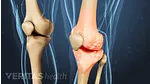
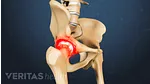
Like almost all medical treatments, there are potential advantages as well as potential drawbacks and uncertainties to using PRP injections to treat osteoarthritis.
In This Article:
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy for Arthritis
- PRP Injection Preparation and Composition
- Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections
- Potential Pros and Cons of PRP Injections
- Choosing a PRP Therapy Doctor
- Who Is a Candidate for Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy?
- Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection Procedure
Advantages of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
There are several reasons why osteoarthritis patients might consider platelet-rich plasma injections:
- Platelet-rich plasma is autologous, meaning it comes from the patient’s body, so it is natural and the injections carry few risks.
- Other treatments for mild to moderate osteoarthritis can be unreliable or vary from person to person, and some have side effects or drawbacks:
- Ways to Get Exercise When You Have Arthritis can often improve but not always eliminate symptoms.
- Cortisone injections are proven to reduce osteoarthritis pain, but repeated injections can weaken ligaments and tendons over time, and may have a detrimental effect on healthy cartilage. 1 Dragoo JL, Danial CM, Braun HJ, Pouliot MA, Kim HJ. The chondrotoxicity of single-dose corticosteroids. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012 Sep;20(9):1809-14. doi: 10.1007/s00167-011-1820-6. Epub 2011 Dec 21. PubMed PMID: 22186921. , 2 Piper SL, Kramer JD, Kim HT, Feeley BT. Effects of local anesthetics on articular cartilage. Am J Sports Med. 2011 Oct;39(10):2245-53. doi: 10.1177/0363546511402780. Epub 2011 Apr 22. Review. PubMed PMID: 21515808.
- Anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDS) such as aspirin and ibuprofen can reduce pain, but long-term use can aggravate stomach problems, blood pressure and heart problems.
- Minor surgeries to treat osteoarthritis, such as arthroscopic debridement, have mixed results, and may be no better than placebo. 3 Kirkley A, Birmingham TB, Litchfield RB, Giffin JR, Willits KR, Wong CJ, Feagan BG, Donner A, Griffin SH, D’Ascanio LM, Pope JE, Fowler PJ. A randomized trial of arthroscopic surgery for osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med. 2008 Sep 11;359(11):1097-107. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0708333. Erratum in: N Engl J Med. 2009 Nov 12;361(20):2004. PubMed PMID: 18784099. , 4 Moseley JB, O’Malley K, Petersen NJ, Menke TJ, Brody BA, Kuykendall DH, Hollingsworth JC, Ashton CM, Wray NP. A controlled trial of arthroscopic surgery for osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med. 2002 Jul 11;347(2):81-8. PubMed PMID: 12110735.
- Joint replacement surgeries are major surgeries that require long-term rehabilitation, and should be reserved for more debilitating cases of arthritis
Read more: Knee Surgery for Arthritis
- While more data are needed, research so far seems to be promising.
Because osteoarthritis has no surefire treatment and there are few risks associated with platelet-rich plasma injections, some doctors believe PRP therapy is worth trying.
See Stem Cell Therapy for Arthritis
Patients should keep in mind that PRP is not a cure-all, and it may be best used in combination with nonsurgical treatments and lifestyle changes, such as physical therapy, weight loss, bracing, and NSAIDs.
Read more about Alternative Treatments for Arthritis
Uncertainties Regarding Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy
It is still unclear exactly how platelet rich plasma helps regeneration, which can lead to further questions regarding when and how to use it.
Though laboratory studies have shown platelet-rich plasma encourages cell regeneration, scientists do not completely understand how or why this happens. Experts still have many questions regarding platelet-rich plasma treatment:
- Indications, i.e. when should this treatment be used? If it is an effective treatment for osteoarthritis, should it be used in the early stages of osteoarthritis or only when all other options are exhausted?
- What are the optimal concentrations of platelets and white blood cells?
- How much platelet-rich plasma should be injected?
- Do certain additives, such as thrombin, make the PRP more effective?
- When and with what frequency should injections be given? Is one injection enough?
- What is the best rehabilitation protocol to use after PRP injection?
Several clinical trials are underway and will help add to the body of knowledge regarding platelet-rich plasma. Until more is known, doctors must answer these questions based on the research data that are available, personal experience, and doctor-patient communication.
- 1 Dragoo JL, Danial CM, Braun HJ, Pouliot MA, Kim HJ. The chondrotoxicity of single-dose corticosteroids. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012 Sep;20(9):1809-14. doi: 10.1007/s00167-011-1820-6. Epub 2011 Dec 21. PubMed PMID: 22186921.
- 2 Piper SL, Kramer JD, Kim HT, Feeley BT. Effects of local anesthetics on articular cartilage. Am J Sports Med. 2011 Oct;39(10):2245-53. doi: 10.1177/0363546511402780. Epub 2011 Apr 22. Review. PubMed PMID: 21515808.
- 3 Kirkley A, Birmingham TB, Litchfield RB, Giffin JR, Willits KR, Wong CJ, Feagan BG, Donner A, Griffin SH, D’Ascanio LM, Pope JE, Fowler PJ. A randomized trial of arthroscopic surgery for osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med. 2008 Sep 11;359(11):1097-107. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0708333. Erratum in: N Engl J Med. 2009 Nov 12;361(20):2004. PubMed PMID: 18784099.
- 4 Moseley JB, O’Malley K, Petersen NJ, Menke TJ, Brody BA, Kuykendall DH, Hollingsworth JC, Ashton CM, Wray NP. A controlled trial of arthroscopic surgery for osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med. 2002 Jul 11;347(2):81-8. PubMed PMID: 12110735.