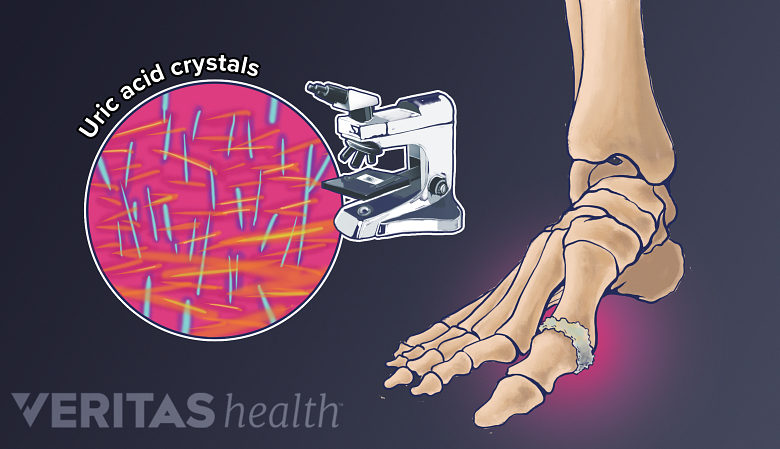
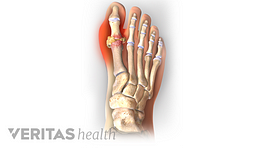
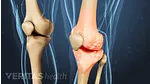
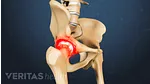
Polyarticular gout and pseudogout cause a build-up of needle-like, microscopic crystals in a joint’s soft tissue. Affected joints can become inflamed and painful, causing people to initially mistake these conditions for rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Gout is a condition caused by the buildup of uric acid in joints and can create symptoms similar to rheumatoid arthritis.
In This Article:
- Are My Painful Joints Caused By Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) or Something Else?
- Is My Joint Pain Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) or Spondyloarthropathy?
- Is My Joint Pain Caused By Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) or a Crystal Arthritis?
- Is My Joint Pain Caused by Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) or an Infection?
- Is My Joint Pain Caused by Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) or Another Autoimmune Disorder?
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Overview Video
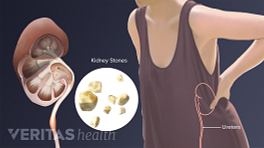
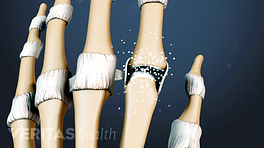
Polyarticular Gout vs. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Gout is a metabolic disorder that causes needle-like, microscopic crystals to build up in a joint. In about 90% of gout cases, only one joint is affected. 1 Harris MD, Siegel LB, Alloway JA. Gout and hyperuricemia. Am Fam Physician. 1999 Feb 15;59(4):925-34. Review. PubMed PMID: 10068714. When it affects two or more joints it is called polyarticular gout.
See All About Gout - Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
How is it similar to RA? Gout causes joint pain, swelling, redness, and warmth, so when it shows up in two or more joints it may be initially mistaken for rheumatoid arthritis. Like RA, gout can cause fever, fatigue, and/or a general feeling of being sick.
How is it different? Gout symptoms usually appear suddenly and without warning. Symptoms often appear at night, waking up a person from sleep. The pain can be excruciating and is typically at its worst within one or two days of initial onset. In contrast, rheumatoid arthritis pain usually appears more gradually and is most notable in the first hour after waking.
See Gout Symptoms
Gout can be diagnosed or ruled out by drawing fluid from the affected joint(s) and examining it under a microscope. People with rheumatoid arthritis rarely get gout.
See Gout Diagnosis
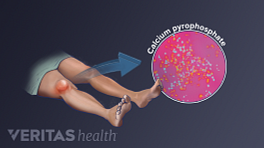
Pseudogout (CPPD) vs. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Like gout, pseudogout symptoms occur when microscopic crystals build up in a joint(s). The medical name for pseudogout is calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition (CPPD) or acute calcium pyrophosphate crystal arthritis (acute CPP crystal arthritis).
See All About Pseudogout - Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
How is it similar to RA? Both diseases can cause joints to be painful, swollen, red and warm. Both RA and pseudogout can affect almost any joint, and both commonly affect the ankles, wrists, large knuckles and knees. People with pseudogout may have a fever.
How is it different? Pseudogout symptoms usually appear suddenly and at any time, with excruciating pain often peaking 6 to 12 hours after symptoms begin. 2 Zhang et al. European League Against Rheumatism recommendations for calcium pyrophosphate deposition. Part I. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 Apr;70(4):563-70. Epub 2011 Jan 7. PubMed PMID: 21216817. In contrast, rheumatoid arthritis pain usually appears more gradually and is most noticeable in the first hour after waking.
Pseudogout can be diagnosed or ruled out by drawing fluid from the affected joint(s) and examining it under a microscope. It will typically go away within two weeks even if left untreated. People with RA can also get pseudogout.
- 1 Harris MD, Siegel LB, Alloway JA. Gout and hyperuricemia. Am Fam Physician. 1999 Feb 15;59(4):925-34. Review. PubMed PMID: 10068714.
- 2 Zhang et al. European League Against Rheumatism recommendations for calcium pyrophosphate deposition. Part I. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 Apr;70(4):563-70. Epub 2011 Jan 7. PubMed PMID: 21216817.